Indian government announced it would be pushing ahead with new rules on cybersecurity. They would require any firms providing cloud services to keep records of the names and IP addresses of their customers for five or more years, and hand it over to the government upon request.
Consumer VPN services fall into this category, but the new laws don’t apply to corporate or enterprise VPNs.
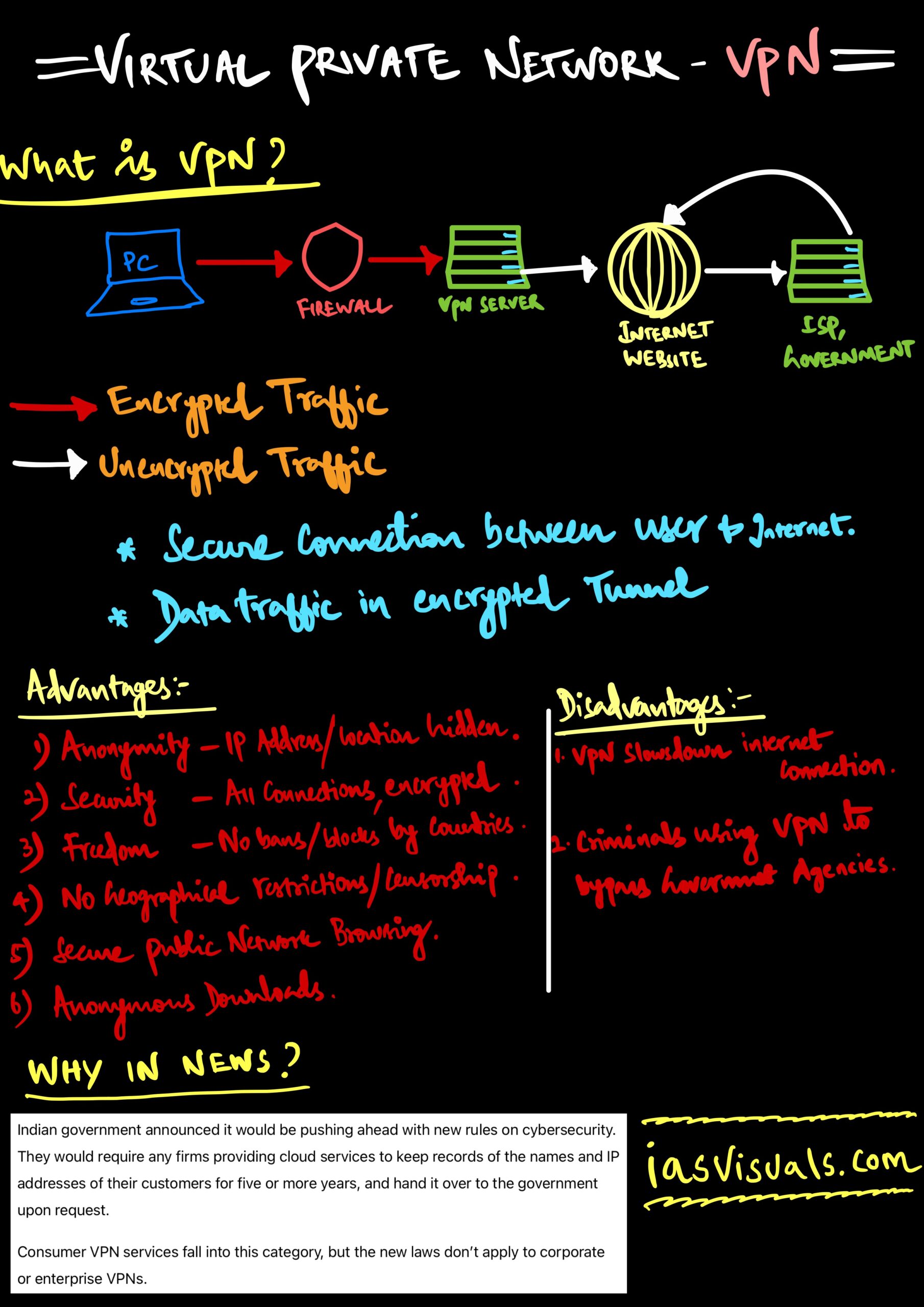
A VPN creates a secure connection between the user and the internet. When you connect to the internet through a VPN, all the data traffic is sent through an encrypted virtual tunnel.
Advantages:
- More Anonymity – Our real IP address and location will be hidden.
2. More Security – All the traffic will be encrypted between the internet and the user.
3. More Freedom – We will be able to access websites and online services that would otherwise be blocked.
What is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network.
When we are using the internet, there is a constant process of your device exchanging data with other parties on the web. A VPN creates a secure tunnel between your device (e.g. smartphone or laptop) and the internet. The VPN allows you to send your data via an encrypted, secure connection to an external server: the VPN server. From there, your data will be sent onward to its destination on the internet.
How a VPN works?
- The VPN software on your computer encrypts your data traffic and sends it to the VPN server through a secure connection. The data also goes through your Internet Service Provider, but they can no longer interact because of the encryption.
- Anonymity Online
- Protection against Hackers and Governments
- Secure browsing on public networks
- Fight online censorship
- Bypass geographical restrictions
- Anonymous downloads
Disadvantages of VPN:
- VPN slow down the internet connection.
- Criminals are using the VPN to escape the Government radar.