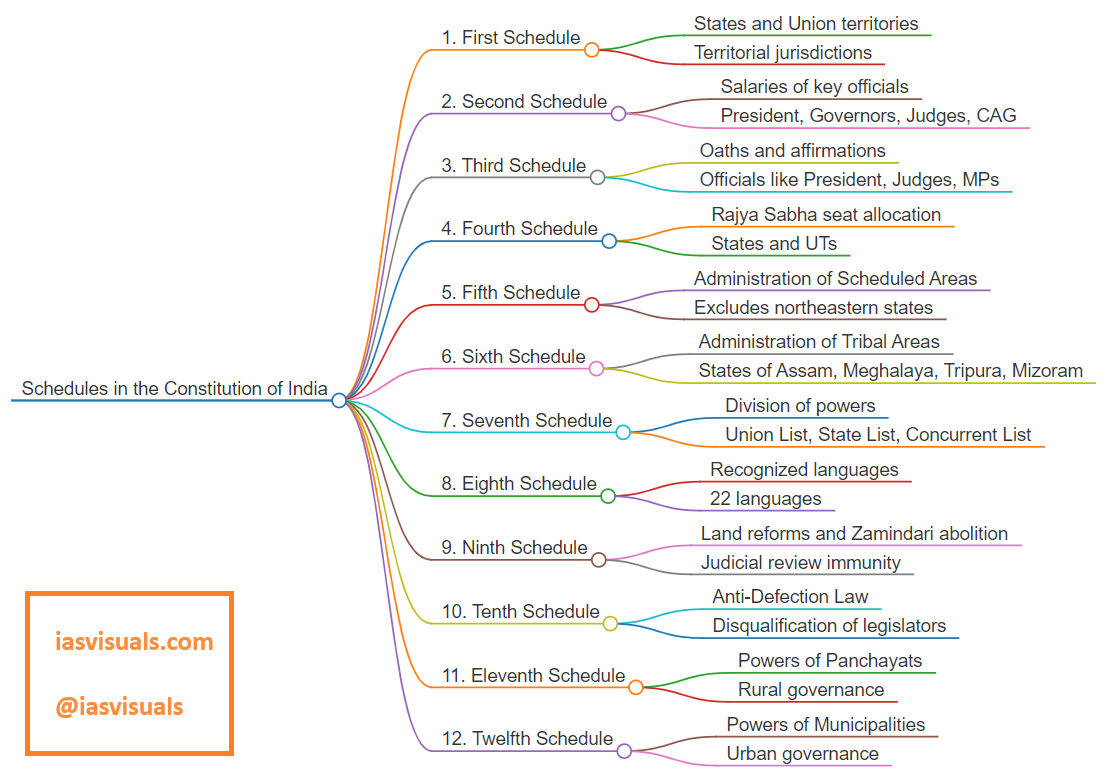
The Constitution of India includes 12 schedules, each addressing specific administrative and legal details. Here’s a brief overview of each:
1. First Schedule: Lists the states and union territories of India, along with their territorial jurisdictions.
2. Second Schedule: Contains provisions regarding the salaries and allowances of the President, Governors, Chief Judges, Judges of the High Court and Supreme Court, Comptroller and Auditor-General.
3. Third Schedule: Includes forms of oaths or affirmations for officials such as the President, judges, and members of Parliament.
4. Fourth Schedule: Allocates seats for each state and union territory in the Rajya Sabha (the Upper House of Parliament).
5. Fifth Schedule: Provides for the administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes in any state except the northeastern states.
6. Sixth Schedule: Details the administration of tribal areas in the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram, allowing for the formation of Autonomous District Councils.
7. Seventh Schedule: Divides powers between the union and the states under three lists—Union List, State List, and Concurrent List.
8. Eighth Schedule: Lists the 22 recognized languages of India.
9. Ninth Schedule: Contains acts and regulations of the state and central legislatures dealing with land reforms and the abolition of the zamindari system. The acts under this schedule are immune from judicial review.
10. Tenth Schedule: Also known as the “Anti-Defection Law,” it lays down the process by which legislators may be disqualified on grounds of defection.
11. Eleventh Schedule: Lists the powers, authority, and responsibilities of Panchayats (village and rural councils).
12. Twelfth Schedule: Details the powers, authority, and responsibilities of Municipalities (urban local government).