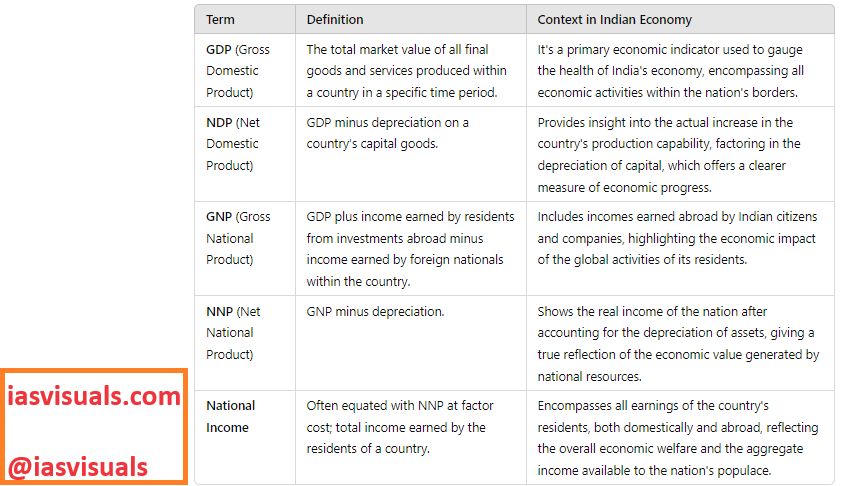
National income and its related concepts like GDP, NDP, GNP, and NNP are crucial for understanding the economic performance of a country like India. Here’s an overview of each of these terms:
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
– Definition: GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a specific time period.
– Context in India: It’s a primary indicator used to gauge the health of India’s economy. It includes all private and public consumption, government outlays, investments, and net exports that occur within India. Economists and policymakers monitor GDP growth as a primary indicator of economic strength and development.
2. Net Domestic Product (NDP):
– Definition: NDP is calculated by taking GDP and subtracting depreciation. Depreciation refers to the wear and tear on an economy’s total capital goods.
– Context in India: NDP provides a clearer measure of the actual increase in the country’s production capability. It’s a better metric when assessing economic performance over time, as it accounts for the aging and degradation of capital.
3. Gross National Product (GNP):
– Definition: GNP is the GDP of a country added with its income earned from overseas investments minus the income earned by foreign nationals within the country.
– Context in India: For India, GNP is significant as it includes the incomes that Indian citizens and businesses earn abroad, which is substantial given the large Indian diaspora and multinational companies.
4. Net National Product (NNP):
– Definition: NNP is derived by subtracting depreciation from GNP. It represents the total value of goods and services produced by the residents of a country in a year minus the loss of value of capital goods due to wear and tear.
– Context in India: NNP gives a more accurate reflection of the country’s economic performance as it accounts for the value lost due to depreciation of assets.
5. National Income:
– Definition: National income is often referred to as NNP at factor cost. It represents the total amount of money earned within a country, including earnings from foreign sources.
– Context in India: National income provides a broad view of the economic strength of the country, taking into account the total income received by residents of the country. It helps in assessing the economic welfare of the citizens.
These metrics are not only indicators of economic health but are also vital for strategic planning and policy-making in India. They help in understanding the level of economic activity, making international comparisons, planning of public expenditures, and guiding fiscal and monetary policies.