Here’s a detailed look at the components of the foreign exchange reserves of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), their current status, historical trends, and future prospects:
Components of Foreign Reserves
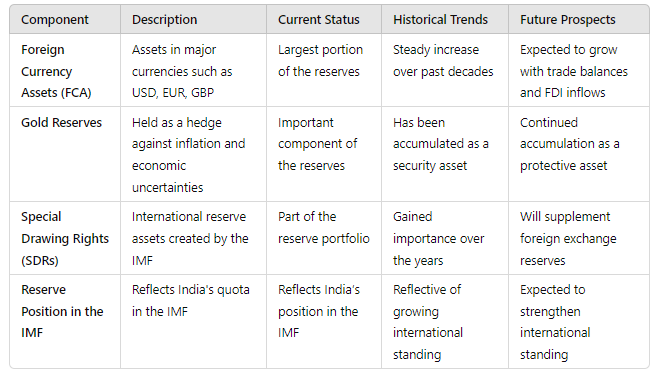
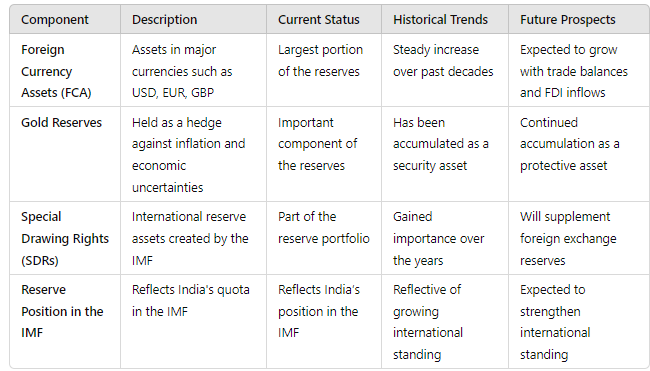
The foreign exchange reserves of India include the following main components:
1. Foreign Currency Assets (FCA): These are assets in major currencies like the US Dollar, Euro, and British Pound and constitute the largest portion of the reserves.
2. Gold Reserves: Held as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties.
3. Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): These are international reserve assets created by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to supplement the official reserves of its member countries.
4. Reserve Position in the IMF: This represents India’s quota in the IMF, reflecting its position and voting power within the institution.
Current Status and Trends
– India’s foreign exchange reserves stood at approximately USD 617.3 billion.
– The reserves have seen a significant increase, with India adding USD 59.7 billion to its reserves during the calendar year 2023, making it one of the largest increments among major foreign exchange reserves holding countries.
– The composition of these reserves includes a diverse mix of currencies, gold, SDRs, and other reserve positions, which provides the country with significant financial stability and liquidity.
Historical Trends
– India’s foreign exchange reserves have experienced substantial growth over the past few decades, from just a few billion dollars in the early 1990s to over USD 600 billion in recent years.
– This growth has been driven by various factors, including increased foreign direct investment, growth in IT and service exports, and prudent economic policies.
Future Prospects
– The RBI continues to manage these reserves strategically to support economic growth, stabilize the currency, and cushion against external shocks.
– The diversification of the reserves into different components and currencies aims to minimize risks associated with changes in global financial conditions.
– Continued accumulation of reserves is expected, influenced by India’s trade balances, FDI inflows, and other macroeconomic factors.
These reserves not only enhance India’s creditworthiness on the global stage but also provide a buffer against economic fluctuations, ensuring that the country can meet its international obligations without any liquidity crisis.