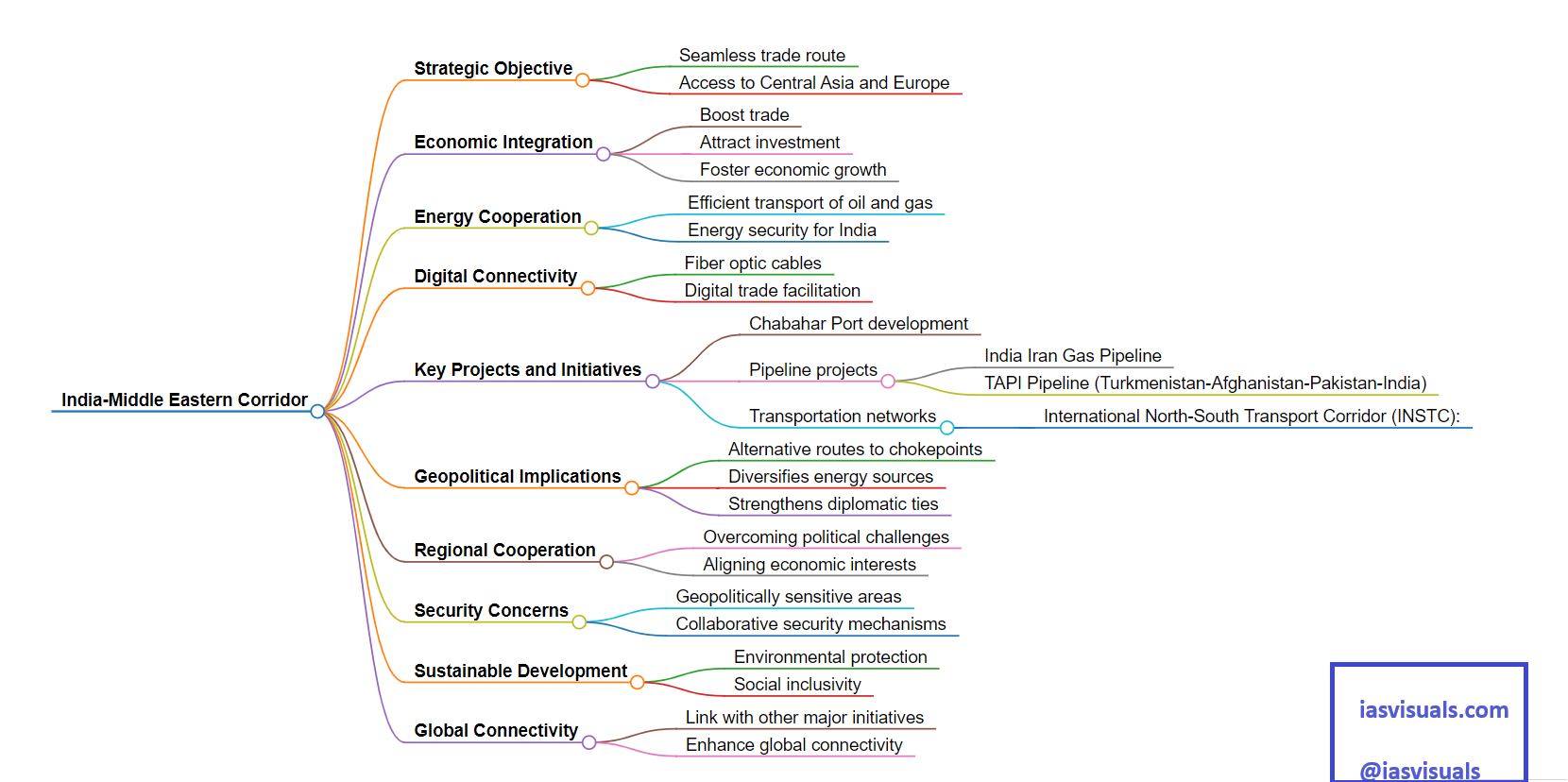
The India-Middle Eastern Corridor, refers to a conceptual and developing network of infrastructure, energy, and digital connectivity projects intended to enhance trade, economic integration, and political cooperation between India, Middle Eastern countries, and possibly extending towards Europe.
1. Strategic Objective:
The corridor aims to create a seamless trade route connecting India with the Middle East, enhancing access to Central Asia and Europe. This includes the development of ports, railways, roads, and pipelines.
2. Economic Integration:
By improving infrastructure and connectivity, the corridor seeks to boost trade, attract investment, and foster economic growth across the regions it encompasses.
3. Energy Cooperation:
Given the Middle East’s vast energy resources, the corridor is crucial for India’s energy security, facilitating the efficient transport of oil and gas to meet its growing energy needs.
4. Digital Connectivity:
Beyond physical infrastructure, there’s an emphasis on digital connectivity, including fiber optic cables and digital trade facilitation, to support the digital economy and innovation.
5. Key Projects and Initiatives:
While specific projects may vary, notable ones include the development of the Chabahar Port in Iran, intended as a gateway for Indian goods heading to Iran, Afghanistan, Central Asia, and beyond. There are also discussions around various pipeline projects and transportation networks.
6. Geopolitical Implications:
The corridor has significant geopolitical implications, as it provides alternative routes to traditional chokepoints controlled by rival powers, diversifies energy sources, and strengthens diplomatic ties.
7. Regional Cooperation:
The success of such a corridor relies on regional cooperation among participating countries, including overcoming political challenges and aligning economic interests.
8. Security Concerns:
The corridor traverses some geopolitically sensitive areas, raising concerns about security and the need for collaborative mechanisms to address potential threats.
9. Sustainable Development:
There’s an increasing focus on ensuring that projects within the corridor promote sustainable development, including environmental protection and social inclusivity.
10. Global Connectivity:
While centered on India and the Middle East, the corridor is part of a larger vision to enhance global connectivity, potentially linking with other major initiatives like the International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and dovetailing with European infrastructure projects.
The India-Middle Eastern Corridor represents a long-term vision with the potential to significantly alter economic and strategic dynamics in the region. Its development will depend on sustained collaboration among the countries involved, addressing both opportunities and challenges along the way.