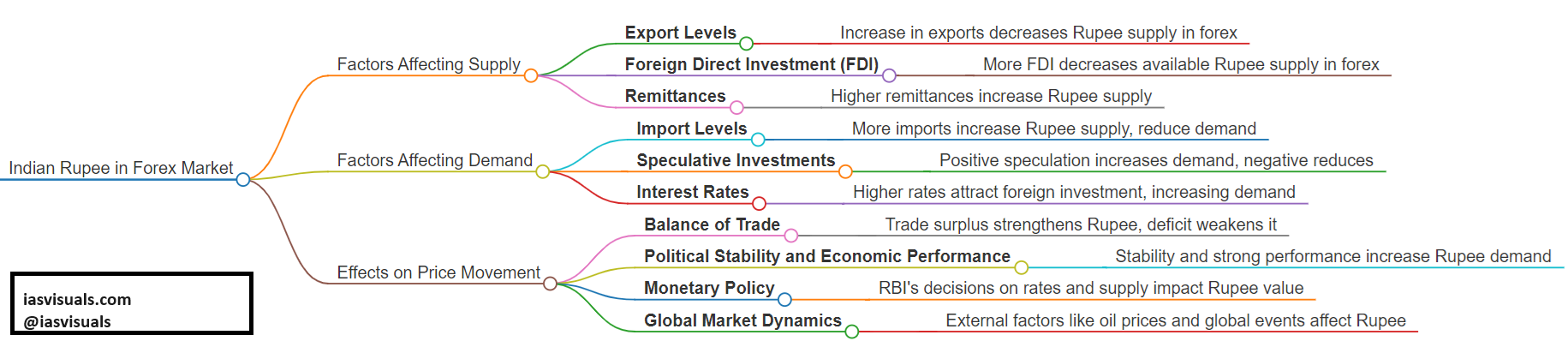
The supply and demand of the Indian Rupee in the forex market are influenced by a variety of factors, and these, in turn, affect its price movement.
Factors Affecting Supply of Indian Rupee
1. Export Levels: Higher exports from India increase the demand for Rupees as foreign buyers need to purchase Rupees to pay for Indian goods, reducing the supply of Rupees in the forex market.
2. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): When India receives foreign investment, investors convert their currency into Rupees, decreasing the supply of Rupees available in the forex market.
3. Remittances: A significant amount of India’s Rupee supply in the forex market is influenced by remittances from Indians living abroad. Higher remittances can increase the supply of Rupees.
Factors Affecting Demand for Indian Rupee
1. Import Levels: When India imports goods and services, it needs to convert Rupees into foreign currencies, increasing the supply and reducing the demand for Rupees.
2. Speculative Investments: Speculation based on the expected performance of the Rupee can affect its demand. Positive speculation increases demand, while negative speculation does the opposite.
3. Interest Rates: Higher interest rates in India compared to other countries can attract foreign investment in Indian assets, increasing demand for the Rupee.
Effects on Price Movement in the Forex Market
– Balance of Trade: A trade surplus (exports greater than imports) typically strengthens the Rupee, while a trade deficit weakens it, affecting its price in the forex market.
– Political Stability and Economic Performance: Political unrest or poor economic performance can reduce investor confidence in the Rupee, lowering its demand and price.
– Monetary Policy: Decisions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regarding interest rates and money supply can directly impact the Rupee’s value. For example, tightening (raising rates or reducing supply) generally supports the Rupee, while easing (lowering rates or increasing supply) might depress its value.
– Global Market Dynamics: External factors such as changes in oil prices (since India is a major importer of oil), global economic trends, and international political events can influence the Rupee’s demand and supply dynamics, thereby impacting its price movement.
These factors collectively determine the short-term and long-term trends in the exchange rate of the Indian Rupee against other currencies in the forex market.