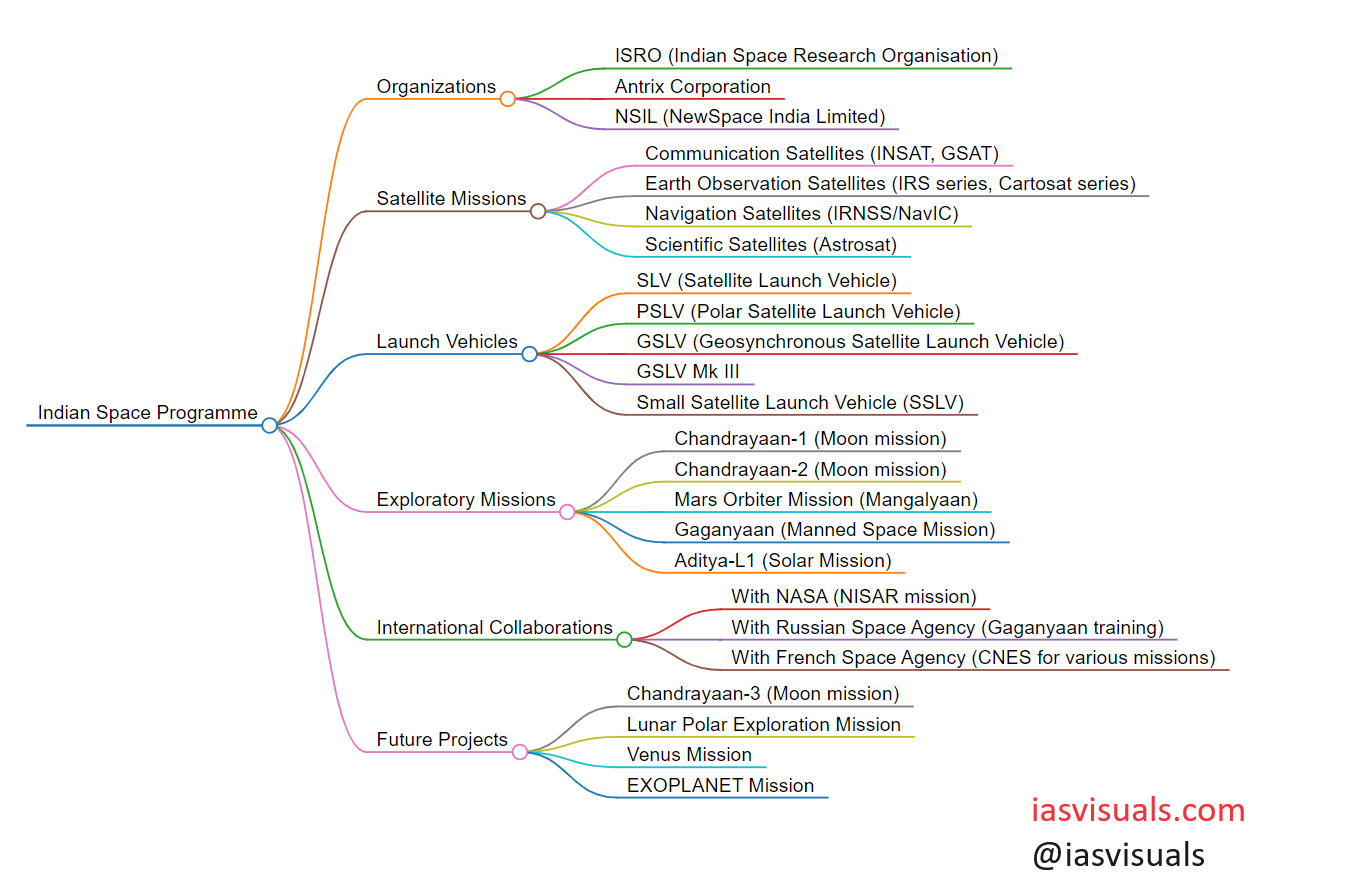
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), founded in 1969, has spearheaded India’s space endeavors, aiming at harnessing space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration. Here’s an overview of its major projects:
Satellite Launch Vehicles
- Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) – India’s first experimental satellite launch vehicle, which successfully deployed the Rohini satellite in 1980.
- Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV) – Developed in the 1980s to deploy satellites into low Earth orbit, demonstrating technologies needed for larger launchers.
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) – A highly successful launch vehicle known for its reliability and versatility, capable of launching satellites into polar and geostationary orbits. It has launched various satellites for India and other countries.
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) – Used to launch heavier payloads into geostationary orbits, including communication and meteorological satellites.
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III) – India’s most powerful launcher, designed to carry heavier payloads into geostationary orbit and play a crucial role in India’s manned space missions.
Satellites
- Aryabhata – India’s first satellite, launched in 1975 by the Soviet Union, marking the beginning of India’s foray into space.
- INSAT series – A series of multipurpose geostationary satellites commissioned in 1983, providing services in telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and search and rescue operations.
- IRS series – A series of remote sensing satellites launched since 1988, used for various applications such as agriculture, forestry, water resources, urban planning, and disaster management.
- GSAT series – Geostationary satellites that provide a variety of communication services across India.
- NavIC – An autonomous regional satellite navigation system that provides accurate position information to users in India and the surrounding region.
Space Exploration
- Chandrayaan-1 (2008) – India’s first lunar probe, which made a significant discovery of water molecules on the moon.
- Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) (2013) – India’s first interplanetary mission, making ISRO the fourth space agency to reach Mars orbit and the first to do so in its initial attempt.
- Chandrayaan-2 (2019) – Aimed at exploring the lunar south pole, it included an orbiter, lander (Vikram), and rover (Pragyan), although the lander failed to make a soft landing.
Human Spaceflight
- Gaganyaan Mission – Planned as India’s first manned space mission, aiming to send a crew of astronauts into space.
Future Projects
ISRO continues to advance its capabilities with projects like:
- Aditya-L1, intended to study the Sun.
- A mission to Venus.
- Further developments in reusable launch vehicles (RLV).
- Expansion of the NavIC system.
- Continued development of next-generation launch vehicles and satellite systems.
ISRO’s programs reflect a comprehensive approach to space exploration, satellite communication, and the development of indigenous technologies, emphasizing its growing stature in global space endeavors.